Vestibulonystagmography (VNG) is a comprehensive diagnostic test used to assess the function of the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance. VNG measures the nystagmus (involuntary eye movements) that occurs in response to specific stimuli, providing valuable information on the function of the inner ear (vestibular system) and central nervous system.
VNG is indicated for patients with symptoms of:
The primary goal of VNG is to determine if the vertigo or dizziness the patient is experiencing is due to a vestibular (peripheral) disorder, a central nervous system issue, or a non-vestibular cause. It helps to:
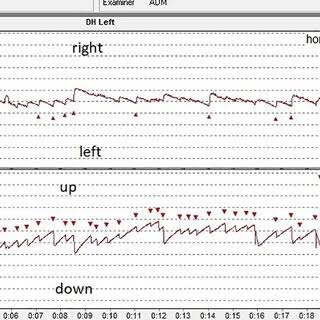
The VNG test is typically performed in the following sequence:
Pre-Test Preparation:
The patient should avoid caffeine, alcohol, and sedatives for at least 24-48 hours before the test, as these can affect results.
The patient is usually advised to stop taking any medications that could interfere with the vestibular system.
The test is often done in a controlled, quiet environment.
Testing:
The patient wears special goggles that track eye movements during the tests.The procedure includes the oculomotor tests, positional tests, and caloric testing. For caloric testing, warm or cold air is introduced into the ear, and the resulting eye movements (nystagmus) are monitored and recorded.
Post-Test Instructions:
The patient may feel dizzy after caloric testing, so it’s important to have someone accompany them for the test, especially if they are driving afterward.
If the patient experiences vertigo during positional testing, it may last only a few seconds.
The functional Head Impulse Test (fHIT) is a diagnostic test used to evaluate the functional status of the vestibular system, specifically the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). It assesses the ability of the eyes to maintain stable vision during rapid head movements, which is crucial for balance and spatial orientation.
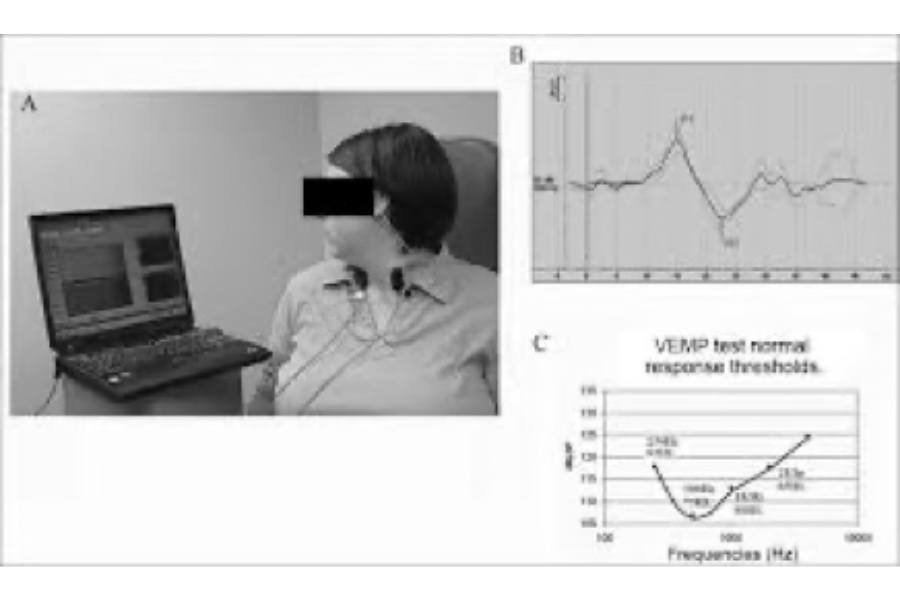
A VEMP test, or Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential test, is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the function of the vestibular system, particularly the saccule and utricle in the inner ear, and their associated nerves. It involves measuring muscle responses to sound or vibration stimuli, helping to identify the causes of dizziness and balance disorders.